A2A ❤️ MCP
TLDR; Agentic applications need both A2A and MCP. We recommend MCP for tools and A2A for agents.
TLDR; 代理应用程序需要 A2A 和 MCP。我们建议将 MCP 用于工具,将 A2A 用于代理。
Why Protocols?(为什么需要协议?)
Standard protocols are essential for enabling agentic interoperability, particularly in connecting agents to external systems. This is critical in two interconnected areas of innovation: Tools and Agents.
标准协议对于实现代理互操作性至关重要,特别是在将代理连接到外部系统时。这在两个相互关联的创新领域中至关重要:工具和代理。
Tools are primitives with structured inputs and outputs and (typically) well-known behavior. Agents are autonomous applications that can accomplish novel tasks by using tools, reasoning, and user interactions. Agentic applications must use both tools and agents to accomplish goals for their users.
工具是具有结构化输入和输出的原语(通常)具有众所周知的行为。代理是自主应用程序,可以通过使用工具、推理和用户交互来完成新任务。代理应用程序必须同时使用工具和代理来实现用户的目标。
Complementary(互补)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is the emerging standard for connecting LLMs with data, resources, and tools. We already observe MCP standardizing ‘function calling’ across different models and frameworks. This is creating an ecosystem of tool service providers and dramatically lowering the complexity to connect agents with tools and data. We expect this trend to continue as more frameworks, service providers, and platforms adopt MCP.
模型上下文协议 (MCP) 是将 LLM 与数据、资源和工具连接起来的新兴标准。我们已经观察到 MCP 在不同模型和框架之间标准化“函数调用”。这正在创建一个工具服务提供商的生态系统,并大大降低了将代理与工具和数据连接的复杂性。我们预计,随着更多框架、服务提供商和平台采用 MCP,这一趋势将继续下去。
A2A is focused on a different problem. A2A is an application level protocol that enables agents to collaborate in their natural modalities. It allows agents to communicate as agents (or as users) instead of as tools. We hope that A2A gains adoption as a complement to MCP that enables ecosystems of agents and will be working in the open with the community to make this happen.
A2A 专注于一个不同的问题。A2A 是一个应用程序级协议,使代理能够以其自然的方式进行协作。它允许代理作为代理(或用户)而不是作为工具进行通信。我们希望 A2A 能够作为 MCP 的补充而获得采用,从而使代理生态系统能够实现这一目标,我们将与社区共同努力实现这一目标。
Example(示例)
Let’s look at an example:
Consider an auto repair shop that fixes cars. The shop employs autonomous workers who use special-purpose tools (such as vehicle jacks, multimeters, and socket wrenches) to diagnose and repair problems. The workers often have to diagnose and repair problems they have not seen before. The repair process can involve extensive conversations with a customer, research, and working with part suppliers.
让我们看一个例子:
考虑一家修理汽车的汽车修理店。该商店雇用使用专用工具(例如千斤顶、多用表和套筒扳手)来诊断和修复问题的自主工人。工人们经常必须诊断和修复他们以前没有见过的问题。维修过程可能涉及与客户、研究和与零件供应商进行广泛的对话。
Now let’s model the shop employees as AI agents:
现在让我们将商店员工建模为 AI 代理:
MCP is the protocol to connect these agents with their structured tools (e.g. raise platform by 2 meters, turn wrench 4 mm to the right).
MCP 是将这些代理与其结构化工具连接起来的协议(例如,将平台抬高 2 米,将扳手向右转 4 毫米)。
A2A is the protocol that enables end-users or other agents to work with the shop employees (“my car is making a rattling noise”). A2A enables ongoing back-and-forth communication and an evolving plan to achieve results (“send me a picture of the left wheel”, “I notice fluid leaking. How long has that been happening?”). A2A also helps the auto shop employees work with other agents such as their part suppliers.
A2A 是使最终用户或其他代理能够与商店员工合作的协议(“我的车发出咔嗒声”)。 A2A 使持续的来回通信和不断发展的计划能够实现结果(“给我发一张左轮的照片”,“我注意到液体泄漏。这种情况持续了多久?”)。 A2A 还帮助汽车商店员工与他们的零件供应商等其他代理合作。
Intersection(交集)
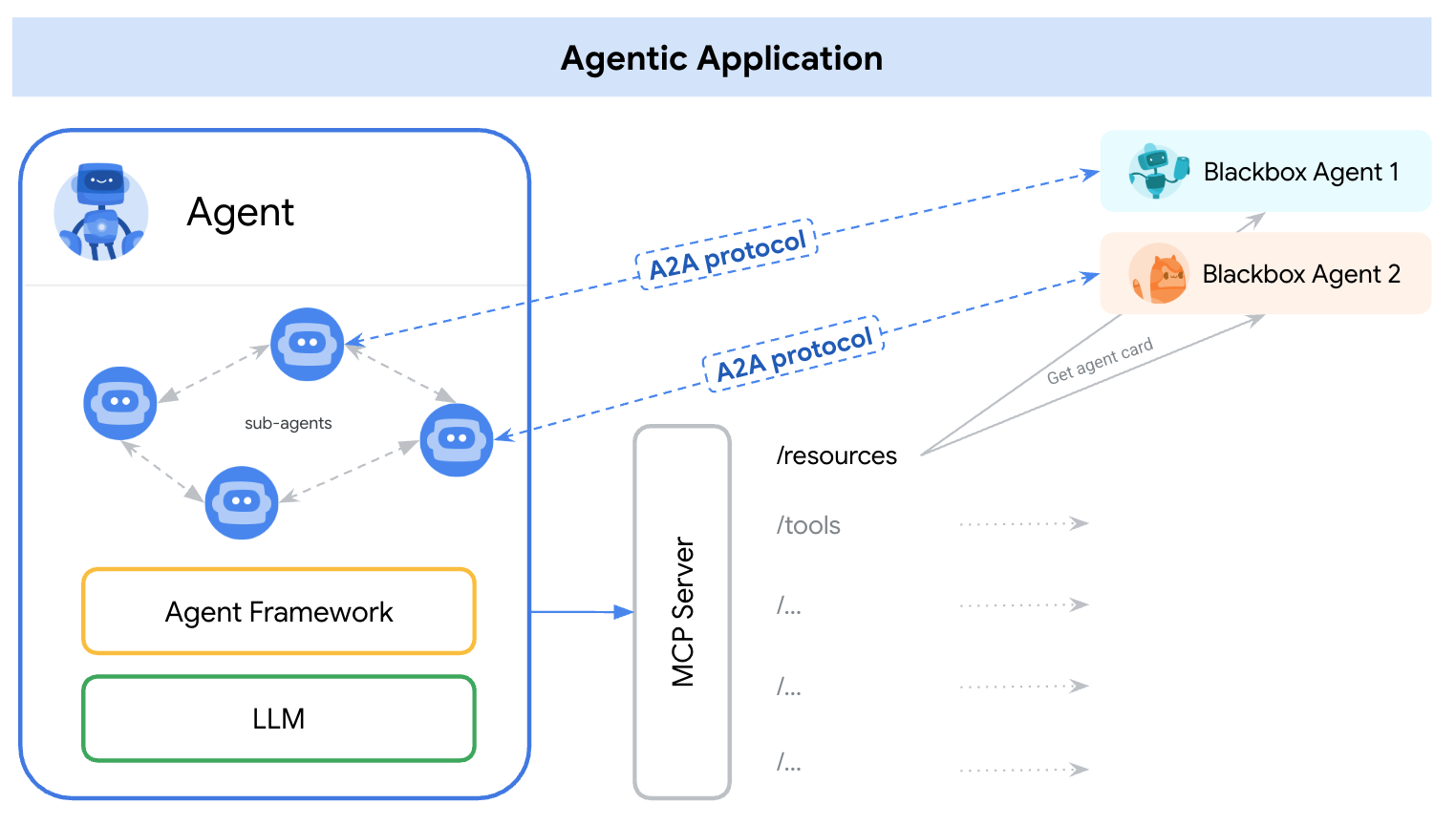
We recommend that applications model A2A agents as MCP resources (represented by their AgentCard). The frameworks can then use A2A to communicate with their user, the remote agents, and other agents.
我们建议应用程序将 A2A 代理建模为 MCP 资源(由其 AgentCard 表示)。 然后,框架可以使用 A2A 与其用户、远程代理和其他代理进行通信。